Varicose Veins During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Pregnancy is a beautiful and transformative experience for many women. However, along with the joy of expecting a new addition to the family, some women may also experience physical discomfort and health challenges. One common issue that can arise during pregnancy is the development or exacerbation of varicose veins.
At Vein Treatment Clinic, we understand the unique concerns and needs of expectant mothers when it comes to vein health. Our board-certified vein doctors carefully examine your leg veins, discuss your symptoms, and offer personalized recommendations to manage vascular health. When and if treatment becomes essential, we only offer minimally invasive spider vein and varicose vein treatments that are considered safe for pregnant women.
You can find our vein treatment clinics across the US, including New York, California, Maryland, and New Jersey. If you’re an expectant mother with spider veins, varicose veins, or signs and symptoms of vein disease, please schedule an appointment at your nearest vein clinic. In this guide, we explore varicose veins during pregnancy, including their causes, symptoms, prevention tips, and available treatment options.
So, What Are Varicose Veins?
Before we delve into varicose veins during pregnancy, let’s start by understanding what varicose veins are. Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that often appear blue or purple. They most commonly occur in the legs and can be both painful and unsightly. Unlike spider veins, which are usually less than 1 millimeter in diameter and remain under the skin’s surface, varicose veins often bulge out of the skin’s surface, looking like dense, knotted rope-like structures.
Varicose veins are usually caused by a condition known as chronic venous insufficiency, which occurs when the one-way valves in your veins become weak or damaged. These valves are responsible for ensuring that blood flows upward toward the heart, preventing it from pooling in the veins. The veins carry deoxygenated blood to the heart, often moving against the force of gravity, and the valves allow one-way circulation. When the valves weaken, blood flows backward and accumulates in the leg veins.
The continued accumulation of blood in leg veins leads to increased pressure and vascular dilation, which eventually leads to varicose veins, spider veins, and other symptoms, such as leg pain, leg heaviness, leg swelling, restless leg syndrome, and frequent leg cramps.
Are you interested in getting more information about your condition or a treatment?
Fill the form below to start!

Why Does Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Varicose Veins?
During pregnancy, a woman’s body undergoes numerous changes to accommodate the growing fetus. Some of these changes can contribute to the development of varicose veins. Here are some of the primary reasons why pregnancy can increase the risk of varicose veins.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in the development of varicose veins during pregnancy. One key hormone involved is progesterone. Progesterone levels rise significantly during pregnancy to support the growth of the placenta and maintain the uterine lining. However, progesterone also has the unintended effect of relaxing the walls of blood vessels, leading to their dilation. This dilation increases the risk of varicose veins.
Increased Blood Volume
To nourish the developing fetus and support the body’s changing needs, the maternal blood volume can increase by up to 50% during pregnancy. The added blood volume can overwhelm the venous system, particularly in the lower limbs, where gravity makes it more challenging for blood to return to the heart. As a result, the veins in the legs may become less effective at propelling blood upwards, leading to venous insufficiency and varicose veins.
Uterine Pressure
As the baby grows, the uterus expands, exerting pressure on nearby organs and blood vessels, including those in the pelvis and lower abdomen. This can impede the flow of blood returning from the legs to the heart. In particular, it affects the iliac veins responsible for transporting blood from the legs to the inferior vena cava. This can lead to a slowdown in venous blood flow, resulting in the pooling of blood in the leg veins and the formation of varicose veins.
Weight Gain
Weight gain is a natural and necessary part of pregnancy as the body stores extra fat and fluids to support the growing baby. However, excess weight can put additional pressure on the veins in the legs. The increased body weight and the pressure exerted by the growing uterus can impede blood circulation in the legs, making it harder for blood to return to the heart. This increases the likelihood of varicose veins developing or worsening during pregnancy.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Varicose Veins During Pregnancy?
Recognizing varicose veins during pregnancy is essential for timely treatment. While the symptoms may vary from person to person, here are some common signs to watch out for:
- Visible Veins: The most apparent sign of varicose veins is the appearance of twisted, bulging veins on the legs, often with a blue or purple hue.
- Leg Swelling: Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet is a common symptom of varicose veins during pregnancy. It typically worsens as the day progresses.
- Aching or Pain: Many expectant mothers experience aching or pain in the legs, especially after standing or sitting for extended periods.
- Itching or Burning Sensation: Varicose veins may cause itching or a burning sensation.
- Muscle Cramps: Some women with varicose veins during pregnancy may also experience frequent muscle cramps in their legs, especially after long periods of sitting or standing.
How Can I Manage Varicose Veins During Pregnancy?
When it comes to treating varicose veins during pregnancy, the approach is typically more conservative compared to non-pregnant individuals. The focus is on managing symptoms and providing relief without exposing the developing fetus to unnecessary risks. Here are some effective ways to manage varicose veins during pregnancy:
- Compression Stockings: Compression stockings are a non-invasive and safe option for managing varicose veins during pregnancy. These specially designed stockings provide gentle pressure to the legs, helping improve blood circulation and reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Leg Elevation: Elevating your legs can help alleviate some of the pressure on your veins. Try to keep your legs elevated above heart level whenever you’re resting.
- Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises like walking and swimming can help improve circulation and strengthen the leg muscles, which can reduce varicose veins.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making simple lifestyle changes, such as avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting, can help prevent varicose veins from worsening.
- Maternity Support Belts: Maternity support belts can provide additional support to the abdomen to reduce pressure on the pelvic veins and relieve varicose vein symptoms.
While the above-mentioned conservative measures can provide relief for many expectant mothers, there may come a point where professional medical intervention is necessary. If you experience severe pain, skin changes around the varicose veins, or bleeding, it’s crucial to consult a vein specialist. Even if you don’t experience severe symptoms, it’s recommended to consult a vein doctor to receive personalized recommendations for the management of varicose veins and to prevent the underlying condition from worsening.
At Vein Treatment Clinic, our board-certified vein doctors are experienced in treating varicose veins during pregnancy while prioritizing the safety of both mother and baby. We perform a thorough evaluation, including physical examinations, symptom assessments, and diagnostic tests. After determining the severity of your vein conditions, we curate personalized treatment plans, which may involve conservative measures to simply manage varicose veins until childbirth or minimally invasive treatments, if necessary.
How Are Varicose Veins Treated?
When conservative measures aren’t sufficient, our vein specialist may recommend minimally invasive vein treatments. Minimally invasive treatments offer effective solutions for varicose veins with shorter recovery times and less discomfort than surgical procedures. Our board-certified vein doctors only offer the safest minimally invasive vein treatments that allow you to resume daily activities immediately without downtime and a negligible risk of complications.
The following are some of the minimally invasive varicose vein treatments we offer:
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLT): EVLT uses laser energy to treat varicose veins. A thin fiber is inserted into the affected vein through a small incision. The laser emits targeted energy that heats and seals the vein shut. As the vein closes, blood is redirected to healthier veins, and the treated vein eventually gets reabsorbed by the body.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA involves using radiofrequency energy to treat varicose veins. A catheter is inserted into the affected vein, where it emits radiofrequency waves that generate heat, causing the vein’s walls to close. Blood flow is rerouted to healthier veins, and the treated vein eventually gets absorbed by surrounding tissue.
- VenaSeal: VenaSeal utilizes a medical adhesive to close off varicose veins. A small amount of the adhesive is injected directly into the affected vein. The adhesive seals the vein shut, and the blood is naturally rerouted through alternative, healthier veins. Over time, the sealed vein becomes fibrotic and is absorbed by the body.
- ClariVein: ClariVein combines mechanical and chemical methods to treat varicose veins. A catheter with a rotating tip is inserted into the vein, and a sclerosing agent is injected. The mechanical action of the rotating tip helps disperse the sclerosing agent. This causes irritation and inflammation in the vein’s walls, leading to its closure and eventual absorption.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Ambulatory phlebectomy removes small varicose veins near the surface of the skin. The procedure involves making tiny incisions over the affected area. The veins are then physically removed through these incisions, often using a hook-like instrument. This technique effectively eliminates the visible varicose veins.
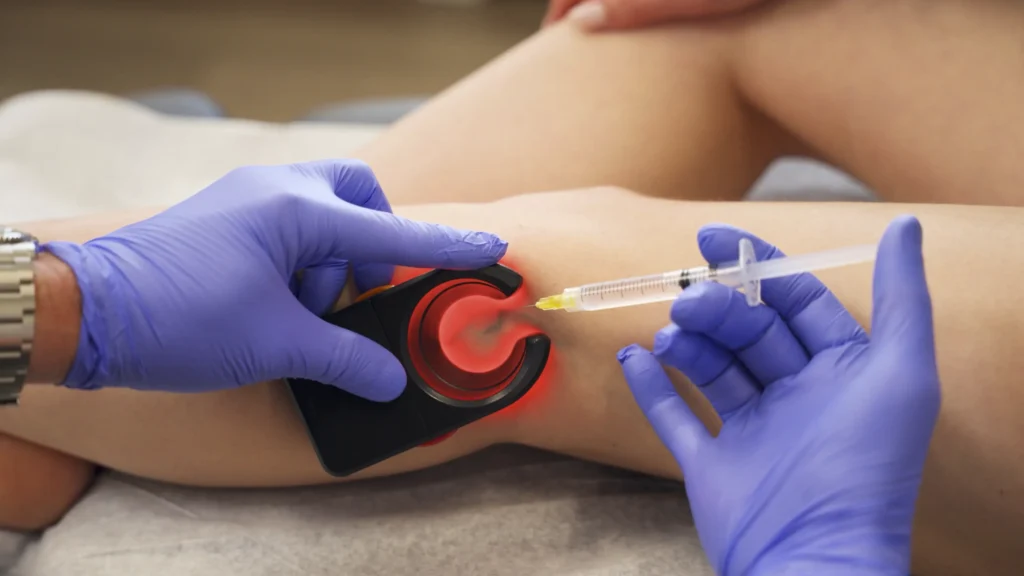
- Sclerotherapy: Sclerotherapy is a commonly used treatment for smaller varicose and spider veins. It involves injecting a specialized solution directly into the affected vein. The solution irritates the vein’s walls, causing them to stick together and eventually collapse. Blood is rerouted through healthier veins, and the treated vein gradually fades.
Minimally invasive treatments are preferred options for many patients due to their effectiveness, minimal discomfort, and shorter recovery times. These procedures target the underlying causes of varicose veins, ultimately improving blood circulation and providing relief from the symptoms associated with this condition. It’s essential to consult with a vein specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment based on your specific condition and medical history.
How Can I Prevent Varicose Veins During Pregnancy?
While not all cases of varicose veins can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and minimize their severity during pregnancy:
- Invest in and wear compression stockings to support your leg veins.
- Engage in regular, low-impact exercises such as walking and swimming.
- Follow a balanced diet and manage your weight within a healthy range.
- Avoid prolonged periods of standing or sitting; take frequent breaks to move your legs.
- Whenever possible, elevate your legs above heart level to alleviate pressure on your veins.
- Opt for comfortable, low-heeled shoes to reduce strain on your leg muscles and veins.
- Sleep on your left side to improve blood circulation by reducing pressure on the major vein that returns blood from your lower body to your heart (the inferior vena cava).
- Drink plenty of water to maintain proper blood volume and prevent blood from thickening.
- Include fiber-rich foods in your diet to prevent constipation, which can increase abdominal pressure and worsen varicose veins.
- Take short breaks to elevate your feet, even when you’re sitting.
- Choose loose-fitting clothing that does not constrict your waist, groin, or legs.
- Flex your ankles and perform leg exercises to help pump blood back towards your heart.
Schedule Your Consultation Today
Varicose veins during pregnancy can be uncomfortable, but they are a common occurrence that many expectant mothers face. Fortunately, there are safe and effective ways to manage and treat varicose veins while prioritizing the health and well-being of both mother and baby.
At Vein Treatment Clinic, we understand the unique challenges and concerns of pregnant women dealing with varicose veins. Our team of board-certified vein doctors is here to provide expert guidance and tailored treatment options to ensure your pregnancy is as comfortable and enjoyable as possible. Remember, if you’re experiencing severe symptoms or have concerns about your varicose veins during pregnancy, don’t hesitate to schedule a consultation.